AWS Lambda Function URLs
2022-04-08
AWS announced a new feature to Lambda, Lambda Function URLs. Here’s a quick rundown of what they are, how they work and two ways of creating them.
What are Lambda function URLs
Previously, if you wanted to expose a Lambda with an HTTP endpoint you would normally use the fully managed API Gateway service, this new feature will instead allow you to have an HTTPS URL that is directly connected to your Lambda function, cutting out the API Gateway middleman.
One great feature is the pricing. Lambda Function URLs are completely “free”. You’ll only ever be paying for the invocation and memory time, like a normal Lambda. This is one advantage over API Gateway which costs to integrate.
However, that doesn’t mean they’re a direct replacement for API Gateway. Instead, API Gateway provides more advanced features such as the ability of JWT/custom authorizers, request-response validation and transformation, usage plans, direct built-in AWS firewall support and more.
How they work
Each URL is unique to a function's alias or the function ARN which would invoke the latest version of the function. This allows you to deploy multiple versions of a function with different URLs for testing and iterative development.
Handling the request is straightforward, the event object you normally use in a Lambda is also populated with properties relating to the HTTP request. For example, you can extract the method from the requestContext.
const method = event.requestContext.http.method;
Any query parameters on the URL can be accessed via a queryStringParameters property.
const queryParam = event.querySTringParameters.myParam;
And, finally, you can access the request body from body property.
const body = event.body;
1. Creating a Lambda URL via ClickOps
You can enable a Function URL from UI when creating a Lambda.
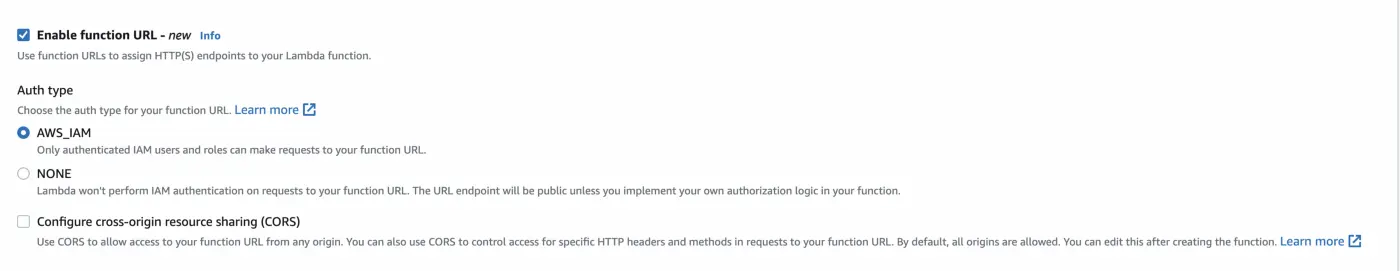
First select advance options and then select Enable function URL.
This will bring up a new set of options where you can see the authentication settings and configure CORS options.
What you will see is a new Function URL parameter on the right-hand side of the function options. This is your function URL.

Your code can now be invoked via a web request without the setup of APIGateway!
2. Creating a lambda URL via Cloudformation
Instead of clicks, we can use Cloudformation to create our URL accessible Lambda. Cloudformation is Amazon's Infrastructure as Code and allows you to programmatically create “stacks” and deploy them to AWS.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description: "Cloudformation template for Lambda"
Resources:
MattsLambda:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Description: my lambda with a url
FunctionName: MattsTestLambda
Handler: index.handler
MemorySize: 128
Runtime: nodejs14.x
Timeout: 5
Role: {{ ADD YOUR ROLE ARN HERE }}
Code:
S3Bucket: mybucket
S3Key: mycode.js
If you’ve created Lambdas before you’ll probably recognise most of the fields above. You’ll notice that we didn’t add a Lambda Function URL field to the properties. That's because Lambda Function URLs are a new type of Resource rather than a field directly on the Lambda function resource.
Instead, to create one we need to add an additional resource and reference back to the URL we’re creating.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description: "Cloudformation template for Lambda"
Resources:
MyLambda:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
Description: my lambda with a url
FunctionName: MattsTestLambda
Handler: index.handler
MemorySize: 128
Runtime: nodejs14.x
Timeout: 5
Role: {{ ADD YOUR ROLE ARN HERE }}
Code:
S3Bucket: mybucket
S3Key: mycode.js
### Lets create the URL ###
MattsLambdaURL:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Url
DependsOn: MyLambda
Properties:
AuthType: NONE
TargetFunctionArn: !GetAtt MyLambda.Arn
We’ve added a new resource of type Lambda::Url. But what you should note is we’re also adding an DependsOn attribute. This attribute will make sure CloudFormation doesn't deploy the URL resource until our Lambda function has been created. This is because it's dependent on the Lambda ARN, you can see we’re referencing it on the final line.
Running the following command in the terminal will create the stack in Cloudformation which then creates the lambda and the URL.
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name MyStackName --template-body file://my-file.yaml
Alternatively, you can upload the stack directly to Cloudformation through the AWS dashboard.
There you have it, a quick rundown on the latest features of AWS Lambda Function URLs and how to implement them yourselves.
Source code: Github
